Hiring the right software engineer is just the beginning. Today that means finding someone that has great coding skills but also the ability to pick up Cursor, Claude Code or other AI-based solutions to make their productivity 2x/3x the one of a normal engineer. Still, it doesn't change the fact that once they’re in, the ...
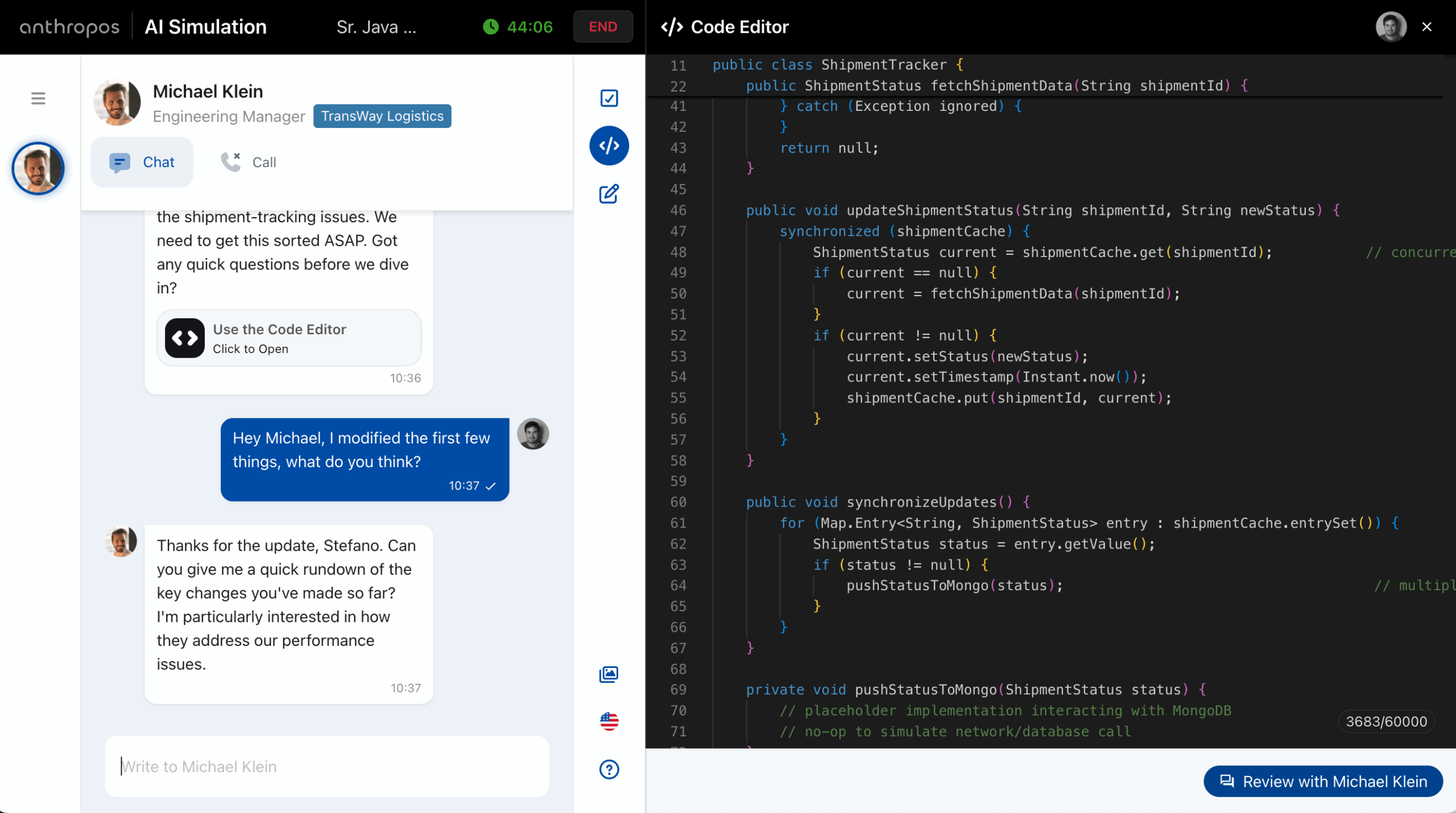
Hiring engineers has never been easy, but in 2025 it’s becoming one of the most complex challenges for companies across industries. The rapid evolution of technology, coupled with the widespread use of AI-assisted tools, has fundamentally changed how software is built—and how developers should be evaluated. In a world where AI is helping developers being ...
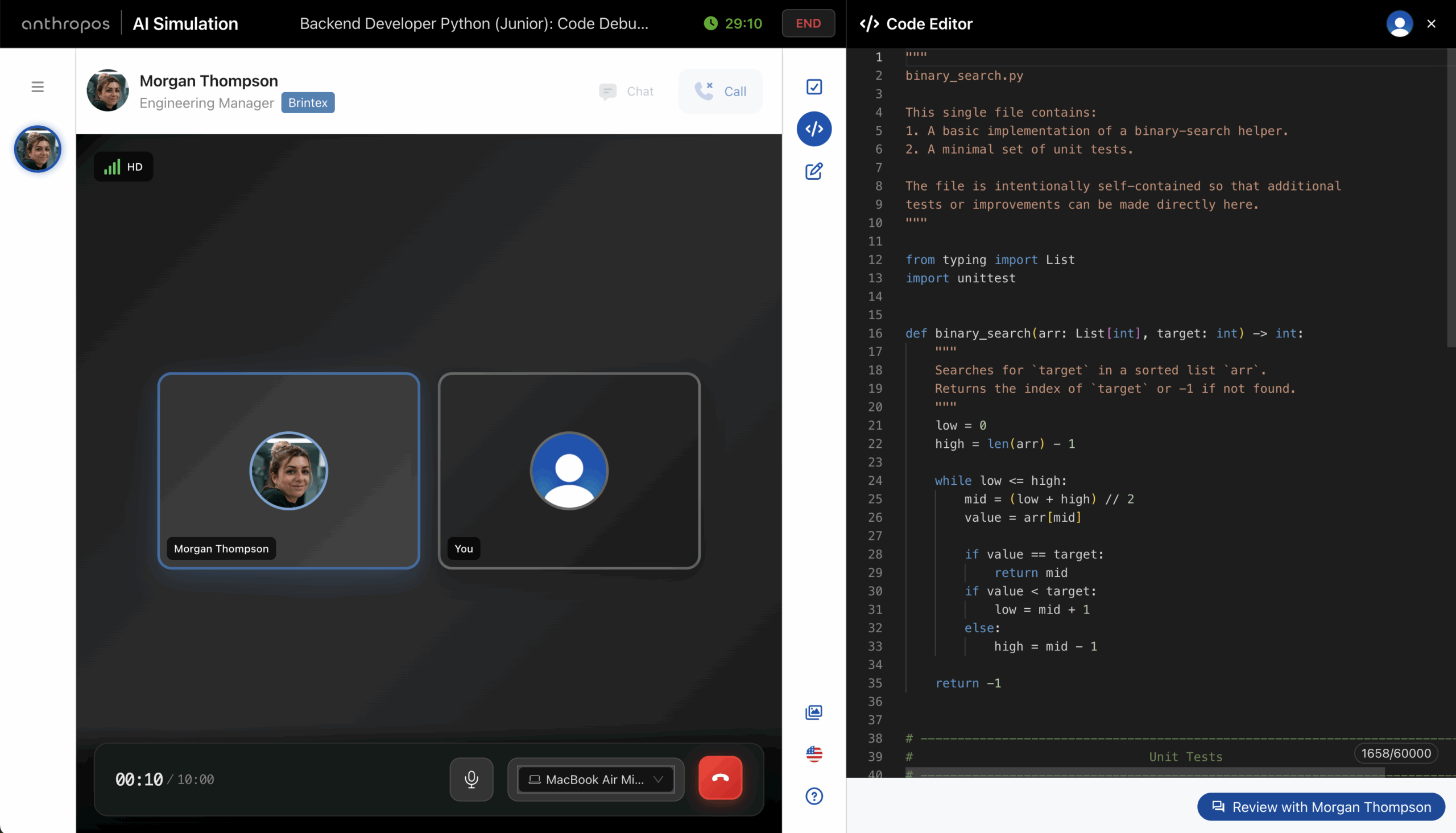
In today’s AI-augmented development landscape, hiring a talented developer is only step one. The harder and more crucial challenge is making sure they stay sharp—ready to adapt to shifting technologies, changing architecture choices, and increasingly cross-functional expectations. The future of software development isn’t just about coding anymore. It’s about learning quickly, collaborating well, navigating ambiguity, ...
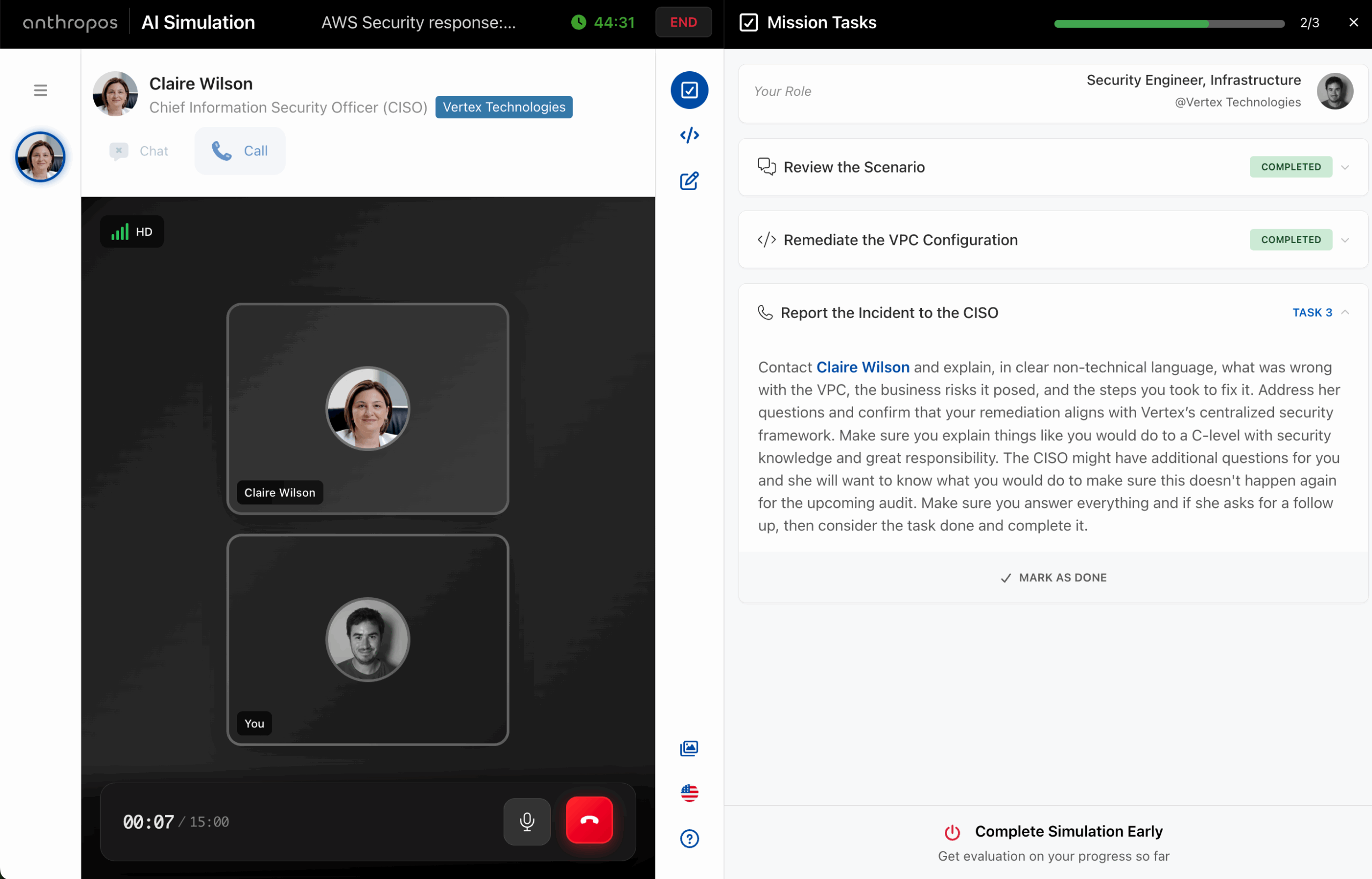
For years, the live coding session has been the gold standard for hiring software engineers, front-end developers, and other technical roles. A candidate joins a Google Meet or Teams call, a couple of senior engineers log in, and for the next hour the candidate is expected to solve coding challenges live, while explaining their thought ...
By Stefano Bellasio
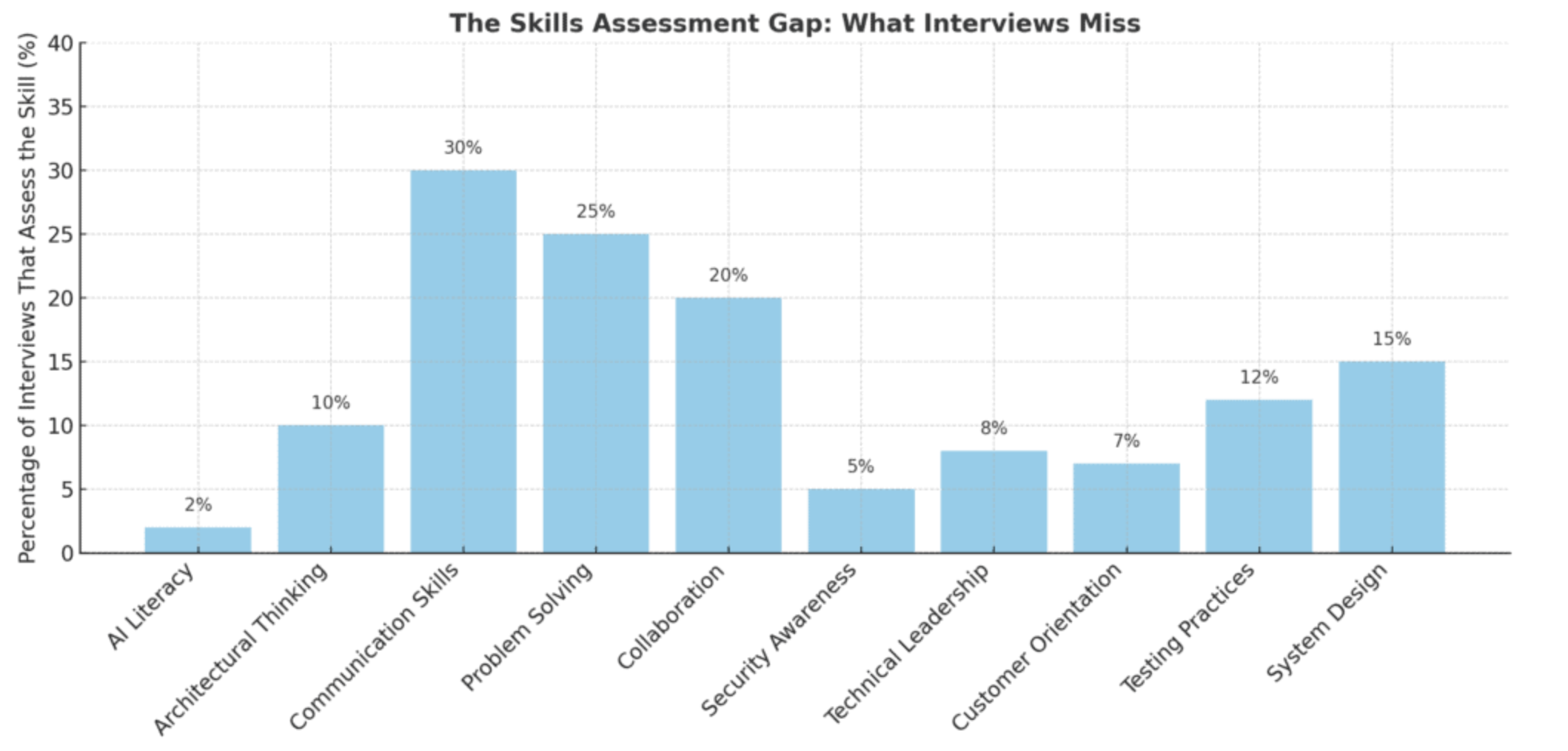
The way companies evaluate and hire software developers is changing faster than ever before. For years, technical hiring relied heavily on coding tests and algorithm challenges—often delivered through platforms like HackerRank or similar tools. These assessments asked candidates to solve abstract problems under time pressure, with the goal of proving raw coding ability. While they ...
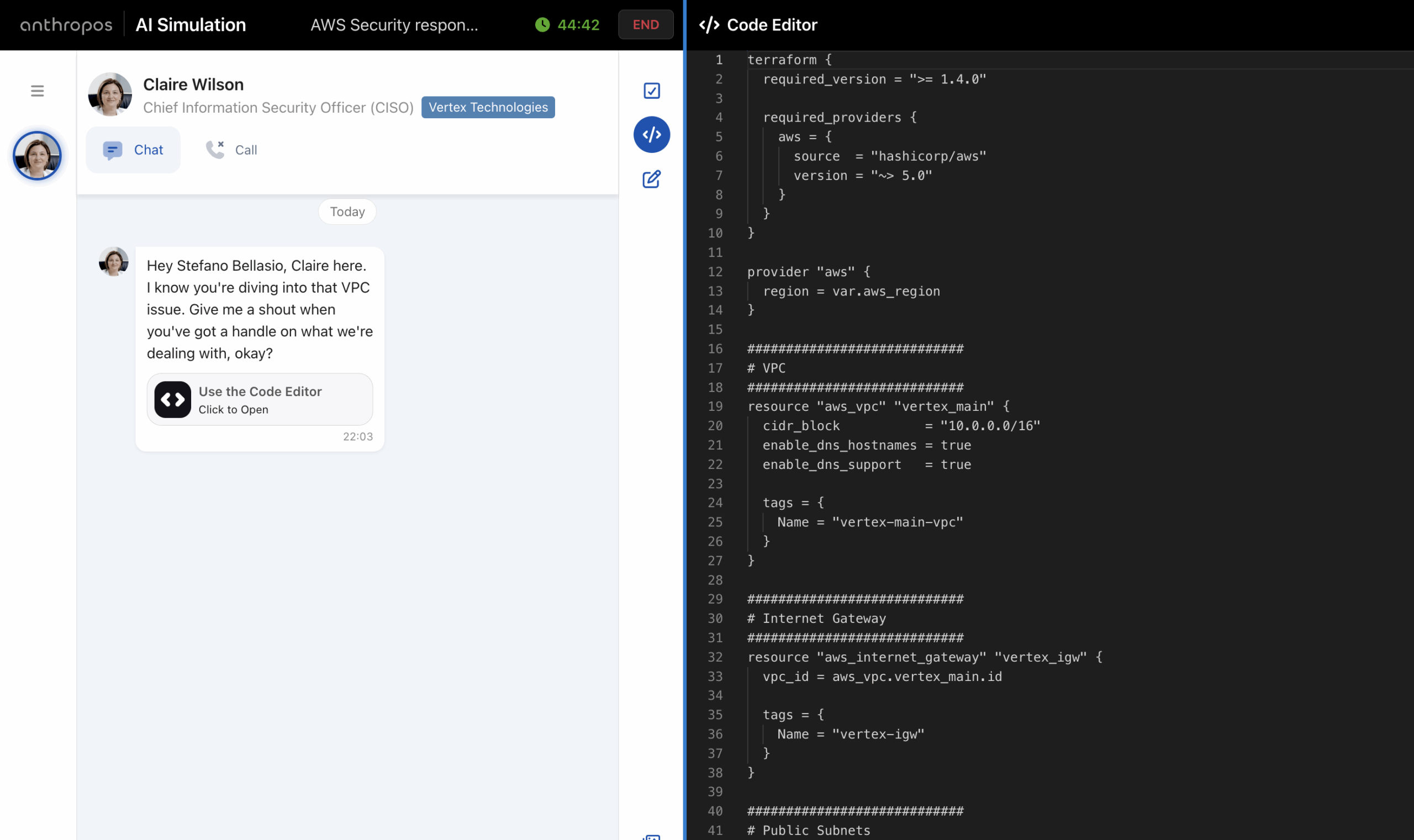
By Stefano Bellasio
Every sales hire you make is a decision that directly affects your bottom line. When done right, it accelerates growth. When done wrong, it drags your numbers down, eats up resources, and can derail entire quarters. That’s why hiring salespeople isn’t just another item on HR’s checklist. It’s a strategic function with real financial consequences ...
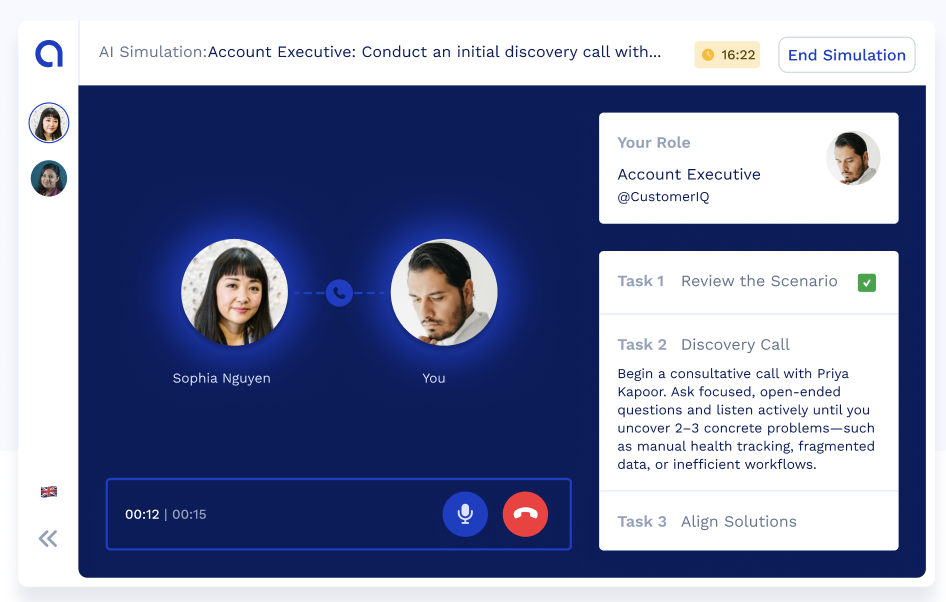
Sales roles are uniquely difficult to hire for. On paper, they seem straightforward: find someone who can communicate, persuade, and close deals. But in reality, sales success relies on a deeper mix of competencies — strategic thinking, adaptability, and resilience under pressure — that are nearly impossible to judge in a traditional interview setting. The ...

By Stefano Bellasio
Hiring the right sales rep can accelerate your revenue. Hiring the wrong one can set you back an entire quarter. Sales is a uniquely high-stakes role. Unlike many functions, its impact is direct, immediate, and measurable. A good rep closes deals, strengthens pipeline, builds trust with prospects, and represents your brand in motion. A poor ...
